When designing a leak-free instrumentation system, one of the first steps to ensuring safety and reliability is to select the right tubing for the intended application. No system integrity is complete without this critical link and its compatibility with the rest of the components. In this post we list four key parameters to consider when selecting quality instrument tube for use with Parker A-LOK® and CPI™ tube fittings.
Parker’s instrument tube fittings have been designed to work in a wide variety of applications that demand the utmost in product performance. Their compatibility with selected tubing is critical for providing consistently high-level of reliability.
1. Material compatibility
The most important consideration in the selection of suitable tubing for any application is the compatibility of the tubing material with the media to be contained. Table 1 lists common materials and their associated general applications. It also lists the minimum and maximum operating temperatures for the various tubing materials.
In addition, Parker instrument fittings are designed to work on like materials. Stainless steel fittings should be used only with stainless steel tubing, 6MO fittings with 6MO tubing, etc. The practice of mixing materials is strongly discouraged.
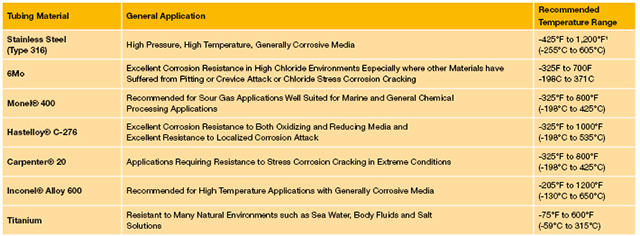
Table 1. Common tubing materials with their applications and operating temperatures.
2. Tubing hardness
The key is to select tube material which is softer than the tube fitting material. For example, Stainless Steel tubing should be specified as Rb 80 or less hardness value. Parker A-LOK® / CPI ™Tube Fittings have, however, been tested on tubing up to Rb 90 hardness level with excellent performance.
3. Wall thickness
Proper wall thickness is necessary to accommodate accepted safety factors relative to desired working pressures. Tube tables published in Parker’s literature, list the tube Outside Diameter (OD) sizes and Wall Thickness combinations per material for safe use with Parker A-LOK® and CPITM tube fittings. Do not use tube with wall thickness values which fall outside of the table ranges.
All working pressures are calculated following the recommendations contained within the ASME B31.3 Chemical Plant and Petroleum Refinery Piping Code and ASME B31.1, Power Piping. All calculations are confirmed via rigorous and extensive testing procedures at our Parker R&D Laboratories. Each calculation utilises an allowable stress figure that incorporates a 4:1 factor of safety.
All testing is carried out to replicate actual working conditions where possible. Parker does not ‘support’ tube to facilitate failure at certain points as this does not truly represent the forces that our products would see in ‘real-time’ applications.
Not all manufacturers support their assemblies’ pressure rating claims with extensive testing. In these cases it is important to understand the implications associated with using unverified recommendations.
Note: Gas Service
Special care must be taken when selecting tubing for gas service. In order to achieve a gas-tight seal, ferrules in instrument fittings must seal any surface imperfections. This is accomplished by the ferrules penetrating the surface of the tubing.
Penetration can only be achieved if the tubing provides radial resistance and if the tubing material is softer than the ferrules. Thick walled tubing helps to provide resistance and the table below provides a range of wall thickness options available for safe use with Parker tube fittings. The ratings in blue indicate the combinations of diameter and wall thickness which are not suitable for gas service.

Table 2. Maximum working pressures (in psig) for imperial tube in 316/316L Stainless Steel material based on tube O.D. size and wall thickness combinations.
4. Elevated temperatures
At elevated temperatures, a de-rating factor should be applied to the working pressure listed in the Parker tube tables. Please see the table below for the de-rating factors for the common materials Parker offers in our A-LOK® tube fittings range.
In all cases, tube fitting assemblies should never be pressurised beyond the recommended working pressure.

Table 3. This table lists the de-rating factors which should be applied to the working pressures for elevated temperature conditions. Simply locate the correct factor in this table and multiply this by the appropriate value in the pressure tables e.g. Table 2 (above) for 316/316L SS.
* Dual-certified grades such as 316/316L, meet the minimum chemistry and the mechanical properties of both alloy grades.
Remember: The Right Tubing + The Right Fitting + SBEx Training = High Integrity Solution.
For more information on Parker’s Instrumentation Tubing, please feel free to fill out our contact form below and a member of KC Controls will be in contact.







